TOPICS
Q&A | Resources | Donor Lymphocyte Infusions | Research News
 Topic Search: PubMed articles Topic Search: PubMed articles
Review | Therapies | Prognosis | Unrelated Donors
In the News
.gif) |
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011 - HLA-C antigen mismatch is associated with worse outcome in unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation.
HLA-C antigen-mismatched unrelated PBSC donors were associated with worse outcomes compared with 8/8 HLA-matched donors.
|
.gif) |
DLBL, relapsed - BjH, 2007: Non-myeloablative (mini) allogeneic stem
cell transplantation for relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a multicentre experience
"Patients with DLBCL who relapse after, or are ineligible for, autologous HCT have a poor prognosis with conventional therapy. This study provides evidence that non-myeloablative allogeneic HCT is an effective salvage therapy which can produce long-term disease-free survival in a subset of these patients. Given that virtually none of these patients would be expected to achieve durable disease-free survival with conventional therapy, the rate of PFS seen after non-myeloablative allogeneic HCT is encouraging and provides proof of the principle that immunological GVL effects alone can control DLBCL in some cases."
|
.gif) |
Be The Match - Patients Connect Facebook Page
People can join the Be The Match Registry® – the world’s largest listing
of potential marrow donors and donated cord blood units – contribute financially and volunteer.
|
Background:
Excellent videos explain the history of stem cell rescue, when it's needed, what it is, and how it's improved over time.
.gif) |
MSKCC About transplants (stem cell rescue) - an excellent overview!
|
.gif) |
MSKCC: Transplant (stem cell rescue) innovations
|
A stem cell transplant* may sometimes be medically necessary for patients with lymphomas.
With a stem cell transplant, the stem cells** obtained from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood are given back to the patient following high dose treatment, which can damage or ablate (kill off) these vital cells. The engrafted stem cells can then restore bone marrow function** impaired or destroyed by the high dose conditioning therapy.
A stem cell transplant is sometimes called a bone marrow transplant.
*The terms stem cell transplant, infusion, rescue, engraftment, or support may be used interchangeably and essentially have the same meaning.
** Stem cells are "immature cells known as hematopoietic or blood-forming stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells divide to form more blood-forming stem cells, or they mature into one of three types of blood cells: white blood cells, which fight infection; red blood cells, which carry oxygen; and platelets, which help the blood to clot.
Most hematopoietic stem cells are found in the bone marrow, but some cells, called peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs), are found in the bloodstream. Blood in the umbilical cord also contains hematopoietic stem cells. Cells from any of these sources can be used in transplants" [in order to restore bone marrow function.] Cancer.gov
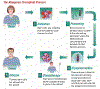 About mini allogeneic transplant This is an allogeneic transplants with reduced intensity conditioning, using less toxic doses of chemotherapy to prepare for the transplant. It relies instead on the killing action of the donor’s immune cells to eradicate the remaining disease. This is sometimes called the Graft vs. Disease (GVD) effect. Click image for an overview of this treatment. About mini allogeneic transplant This is an allogeneic transplants with reduced intensity conditioning, using less toxic doses of chemotherapy to prepare for the transplant. It relies instead on the killing action of the donor’s immune cells to eradicate the remaining disease. This is sometimes called the Graft vs. Disease (GVD) effect. Click image for an overview of this treatment.
A mini transplant has many names:
.gif) |
Reduced intensity Transplant
|
.gif) |
non-ablative or non-myeloablative transplant,
|
.gif) |
Adoptive immunotherapy.
"Non-myeloablative", because the conditioning therapy does not fully ablate (kill off) the bone marrow myeloid cells prior to the engraftment or transplant phase of therapy.
|
...."adoptive immunotherapy", because the donor immune cells act against the disease - a graft versus lymphoma affect.
Concept of graft versus lymphoma effect
"The concept of utilizing enhanced immunosuppression rather than myeloablative cytotoxic conditioning has allowed the engraftment (acceptance) of allogeneic stem cells from related and unrelated donors with lower early transplant-related mortality (TRM) and morbidity.
This approach shifts tumor eradication to the graft-vs-host immune response directed against minor histocompatibility antigens expressed on tumor cells.
This is not without risk, as the long-term effects of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), it’s treatment, or resulting complications and immunodeficiency may be life threatening. However, this approach does allow the application of a potentially curative procedure to elderly or medically infirm patients who would not tolerate high-dose conditioning regimens." - Asheducationbook.org
Chimerism, a term used often in connection with mini-transplants, means the coexistence of donor and recipient cells.
Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell (PBS) Transplantation:
Questions and Answers Cancer.gov
1) What are bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells? Cancer.gov
2) What are bone marrow transplantation and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation? Cancer.gov
3) Why are transplants used in cancer treatment? Cancer.gov
4) What types of cancer are treated? Cancer.gov
5) How are the donor’s stem cells matched to the patient’s stem cells in allogeneic or syngeneic transplantation? Cancer.gov
6) How is bone marrow obtained for transplantation? Cancer.gov
7) How are peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) obtained for transplantation? Cancer.gov
8) How are umbilical cord stem cells obtained for transplantation? Cancer.gov
9) Are any risks associated with donating bone marrow? Cancer.gov
10) Are any risks associated with donating PBSCs? Cancer.gov
11) How does the patient receive the stem cells during the transplant? Cancer.gov
12) Are any special measures taken when the cancer patient is also the donor (autologous transplant)? Cancer.gov
13) What happens after the stem cells have been transplanted to the patient? Cancer.gov
14) What are the possible side effects of BMT and PBSCT? Cancer.gov
15) What is a “mini-transplant”? Cancer.gov
16) What is a “tandem transplant”? Cancer.gov
17) How do patients cover the cost of BMT or PBSCT? Cancer.gov
18) What are the costs of donating bone marrow, PBSCs, or umbilical cord blood? Cancer.gov
19) Where can people get more information about potential donors and transplant centers? Cancer.gov
Resources and Research News:
.gif) |
min-SCT for FL: Haematologica. 2010 Reduced intensity conditioning HLA identical sibling donor allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with follicular lymphoma: long-term follow-up from two prospective multicenter trials
"We conclude that this strategy of reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation may be associated with significant non-relapse mortality in heavily pre-treated patients with follicular lymphoma, but a remarkably low relapse rate. Long-term survival is likely in patients without progressive or refractory disease at the time of transplantation."
|
.gif) |
min-SCT for HL: Superiority of reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation over conventional treatment for relapse of Hodgkin's lymphoma following autologous stem cell transplantation
|
This study compares outcome of reduced-intensity conditioned transplant (RIT) with outcome of conventional non-transplant therapy in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma relapsing following autograft.
There were 72 patients in two groups who had relapsed, and received salvage therapy with chemotherapy radiotherapy.
One group (n=38) then underwent alemtuzumab-containing RIT. The second group-historical controls (n=34), relapsing before the advent of RIT-had no further high-dose therapy.
This group was required to respond to salvage therapy and live for over 12 months post-relapse, demonstrating potential eligibility for RIT, had this been available.
Overall survival (OS) from diagnosis was superior following RIT
(48% at 10 years versus 15% ; P=0.0014),
as was survival from autograft
(65% at 5 years versus 15% ; P0.0001).
For the RIT group, OS at 5 years from allograft was 51% , and in chemoresponsive patients was 58% , with current progression-free survival of 42% .
Responses were seen in 8 of 15 patients receiving donor lymphocyte infusions (DLI) for relapse/progression, with durable remission in five patients at median follow-up from DLI of 45 months (28-55).
These data demonstrate the potential efficacy of RIT in heavily pre-treated patients whose outlook with conventional therapy is dismal, and provide evidence of a clinically relevant graft-versus-lymphoma effect.
full text: www.nature.com
.gif) |
Expert Background: Reduced-Intensity Regimens in Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia asheducationbook 2006 pdf
|
Summary: The current data collectively suggest that addition of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies significantly improves the outcome of autologous SCT in patients with NHL who have chemosensitive disease (Table 3). It is recommended for patients with DLCL or Follicular Lymphoma undergoing their first relapse and MCL during first remission, but not in patients with CLL. [Lay comment: But not necessarily the standard of care for any histology.]
A significant Graft versus Lymphoma effect can be achieved clinically through the use of non-myeloablative transplantation in patients with chemo-sensitive advanced disease. Yet the applicability of non-myeloablative SCT appears dependent on disease histologic type, individual patient, and disease characteristics. The current data suggest an increased risk of relapse with the use of alemtuzumab.
Randomized studies may allow the comparison of various non-myeloablative transplantation strategies. High-dose conditioning regimens should be considered for patients with chemo-refractory (resistant) disease who are young and have a good performance status. The field offers significant opportunity for clinical research, and we strongly encourage participation in clinical trials whenever possible.
.gif) |
Outcomes: "Mini" Allogeneic stem cell transplantation can induce durable clinical and molecular remissions in relapsed lymphomas: pre-transplant disease status and histotype heavily influence outcome. Abstract
|
The results show that frequencies were as follows: cumulative NRM at 3 years, 14%; acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) 35 and 52%, respectively; 3-year overall survival (OS), 69% for LG-NHL, 69% for HG-NHL, 45% for MCL and 32% for HD (P=0.058); and 3-year relapse incidence, 29, 31, 35 and 81%, respectively (P<0.001). Relapse risk differed significantly at 3 years between follicular lymphoma (FL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (14 versus 46%, P=0.04). Molecular remission occurred in 94 and 40% (P=0.002) of patients with FL and CLL, respectively. On multivariate analysis, OS was influenced by chemorefractory disease (hazard ratio (HR)=3.6), diagnosis of HD (HR=3.5), and acute GVHD (HR=5.9). RIC allogeneic SCT is a feasible and effective salvage strategy in both indolent and aggressive NHL.
.gif) |
Cure word used: Mini-BMT: follicular Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Cure? www.webmd.com
83% in Complete Remission 5 to 9 Years After Mini-BMT for Follicular Lymphoma
|
.gif) |
SCT for Low grade Lymphoma asheducationbook.org /2004 full text | PAL's readable version
|
.gif) |
Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Regimens for Hematologic Malignancies: asheducationbook.org
What Have We Learned over the Last 10 Years? (2005) , Sergio Giralt
|
.gif) |
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation (2002) asheducationbook.org
David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon and Judith A. Shizuru
|
.gif) |
According to a recent article published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, "mini"
allogeneic stem cell transplants may provide a chance for a cure for patients over 60 years of
age with poor-prognosis myeloid (blood) malignancies. cancerconsultants.com
|
.gif) |
Nonmyeloablative (mini) Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies: A Systematic Review from Cancer Control: Journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center Medscape (free login req.) 3_5_03
|
.gif) |
Mini transplants - A good readable description BMT infoNet
This type of transplant relies on graft vs disease and uses lower doses of chemo than other transplant regimes.
|
.gif) |
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation (Posted Nov_28_02)
David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon and Judith A. Shizuru asheducationbook.org
|
.gif) |
Nonmyeloablative Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies:
A Systematic Review from Cancer Control: Journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center - Posted 03/05/2003 Medscape
Benjamin Djulbegovic, MD, PhD, Jerome Seidenfeld, PhD, Claudia Bonnell, BSN, MLS,
Ambuj Kumar, MD, MPH
|
.gif) |
Transplant May Help Incurable Lymphomas - Less Toxic Treatment Appears to Cure Some Patients
ACS 01_22_03
|
.gif) |
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation (Posted Nov_28_02),
by David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon and Judith A. Shizuru
asheducationbook.org
|
.gif) |
Patient SCT Stories - Cyberfamily | What to take to Hospital Cyberfamily
|
.gif) |
Less toxic bone marrow transplant technique may have more powerful anti-cancer effect
Researchers induce "chimeric" immune system in lymphoma patients harvard.edu
|
.gif) |
Re-immunization after SCT
|
Research News:
.gif) |
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation in follicular lymphoma: recent progress and controversy http://bit.ly/9QY8aa
"Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo HCT) is a curative treatment for follicular lymphoma, but is hampered by a relatively high treatment-related mortality and by difficulties in identifying high-risk groups for whom transplant is warranted."
|
.gif) |
Mini-allo SCT for relapsed DLBC Lymphoma: a multicentre experience http://bit.ly/a8hDdq
|
.gif) |
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation following reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) can induce durable clinical and molecular remissions in relapsed lymphomas: pre-transplant disease status and histotype heavily influence outcome nature.com
Relapse risk differed significantly at 3 years between follicular lymphoma (FL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (14 versus 46%, P=0.04). Molecular remission occurred in 94 and 40% (P=0.002) of patients with FL and CLL, respectively.
On multivariate analysis, OS was influenced by chemorefractory disease (hazard ratio (HR)=3.6), diagnosis of HD (HR=3.5), and acute GVHD (HR=5.9). RIC allogeneic SCT is a feasible and effective salvage strategy in both indolent and aggressive NHL
|
.gif) |
Reduced Intensity Conditioning Regimens nature.com
Low transplant-related mortality after second allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplant with reduced-intensity conditioning in adult patients who have failed a prior autologous transplant
With a median follow-up of 358 days (450 in 29 survivors), the 1-year incidence of TRM was 24%, and the 1-year overall (OS) and progression-free survival were 63% and 57%, respectively.
|
.gif) |
Review article: Reduced-intensity transplantation for lymphoma.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006 Jul;7(4):295-305. Review. PMID: 16916490
transplant-related morbidity and mortality and graft-versus-host disease remain major obstacles, and future efforts should focus on minimizing risks and more clearly identifying patient-specific and disease-specific predictors of outcome.
|
.gif) |
Outcome report (2007): Long-term outcomes after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for low-grade lymphoma: a survey by the French Society of Bone Marrow Graft Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (SFGM-TC). Haematologica. 2007 May;92(5):627-34. PMID: 17488686
In patients in CR, PR and chemoresistant disease, the 3-year overall survival rates were 66%, 64% and 32%, respectively, while the 3-year event-free survival rates were 66%, 52% and 32%, respectively. The 3-year cumulative incidences of TRM were 32%, 28% and 63%, respectively. The incidence of relapse was 9.6%.
INTERPRETATION AND CONCLUSIONS: Although associated with significant TRM, RIC allogeneic SCT in advanced chemosensitive disease leads to long-term survival.
|
.gif) |
Optimization of allogeneic transplant conditioning: not the time for dogma nature.com
H J Deeg1,2, M B Maris1,2, B L Scott1,2 and E H Warren1,2
"As patients age, their biologic reserve declines, and the capacity to repair tissue and organ damage decreases. At the same time, however, the probability of developing malignancies increases (although recent research suggests that the senescence of cells, which underlies the reduced repair capacity, may provide protection against cancer). Nevertheless, older patients are more likely to suffer from comorbid conditions, which will affect the candidacy for transplantation.5, 22, 23 Reduced-intensity regimens are better tolerated ..."
|
.gif) |
Outcome report (2006): Stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning regimens: a review of ten years experience with new transplant concepts and new therapeutic agents nature.com
Leukemia (2006) 20, 1661–1672. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404334; published online 27 July 2006
A J Barrett1 and B N Savani1
The realization in the 1990s that allogeneic stem cell transplants (SCT) have a potentially curative graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect in addition to the antileukemic action of myeloablative conditioning regimens was a major stimulus for the development of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens, aimed primarily at securing engraftment to provide the GVL effect, while minimizing regimen-related toxicity. It is now over 10 years since RIC regimens were heralded as a new direction in the field of SCT.
|
.gif) |
Non-Myeloablative Allogeneic Hematopoietic Transplantation in Relapsed/Primary Refractory Follicular Lymphoma. Session Type: Poster Session 522-II ASH 2004
"non-myeloablative" means pretreatment (conditioning phase of treatment) that has lower toxicity and does not ablate (kill off) the myeloid cells in the marrow. Often called a mini-transplant. "Allogeneic" means from a donor, in this case an HLA-identical sibling. "Hematopoietic" means the process of forming blood cells from stem cells in the bone marrow.
|
.gif) |
Nonmyeloablative Allogeneic Hematopoietic Transplantation [mini]: A Promising Salvage Therapy for Patients With Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Whose Disease Has Failed a Prior Autologous Transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2004 Jun 15;22(12):2419-23. PMID: 15197204
|
.gif) |
About - Related PubMed Abstracts
|
.gif) |
Description BMT infoNet
|
.gif) |
HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2003 Sep 15;102(6):2021-30. Epub 2003 Jun 05. PMID: 12791654 | More
|
.gif) |
Tandem Transplants: Patients with mantle-cell lymphoma relapsing after autologous stem cell transplantation may be rescued by allogeneic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000 Sep;26(6):677-9. PMID: 11035375 PubMed
|
.gif) |
Nonablative allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation as adoptive immunotherapy for indolent lymphoma: low incidence of toxicity, acute graft-versus-host disease, and treatment-related mortality. Blood. 2001 Dec 15;98(13):3595-9. PubMed
|
|